Dark Matter Matters
Red Hat
Maslow’s hierarchy of (community) needs
Over the past month or so, I’ve been having a conversation with Iain Gray, Red Hat Vice President of Customer Engagement, about the ways companies engage with communities. I’ve also written a lot lately about common mistakes folks make in developing corporate community strategies (see my two posts about Tom Sawyer community-building here and here and Chris Brogan’s writeup here).
One idea we bounced around for a while was a mashup of community thinking and Maslow’s hierarchy of needs. For those of you who slept in with a bad hangover the day you were supposed to learn about Maslow in your intro psych class (damn you, Jagermeister!), here is the Wikipedia summary:
“[Maslow’s hierarchy of needs] is often depicted as a pyramid consisting of five levels: the lowest level is associated with physiological needs, while the uppermost level is associated with self-actualization needs, particularly those related to identity and purpose. The higher needs in this hierarchy only come into focus when the lower needs in the pyramid are met. Once an individual has moved upwards to the next level, needs in the lower level will no longer be prioritized. If a lower set of needs is no longer being met, the individual will temporarily re-prioritize those needs by focusing attention on the unfulfilled needs, but will not permanently regress to the lower level.”
Now granted, the needs of a company are very different than the needs of a human being. At its very basic level, a company has a “physiological” need to make money. If that need is not being met, little else will matter. But in an ironic twist, this basic need to make money can actually hinder the company’s ability to make money if it is not wrapped in a more self-actualized strategy.
To explain what I mean, think about the last annoying salesperson who called or emailed you. Why were you annoyed? Probably because it was very clear to you that the salesperson was badly hiding his basic motivation to make money. He wasn’t talking to you because he valued you– he was talking to your wallet.
Now think about the best recent sales experience you’ve had. Mostly likely, this salesperson was being motivated by a higher purpose, perhaps something as simple as a desire to make you happy. Sometimes the most effective salespeople aren’t even in sales at all– like a friend who tells you about a new album you should buy, for example. Or sites like Trip Advisor, where you can learn about where to go on vacation from other folks like you.
When it comes to community strategy, most companies have trouble finding motivation beyond the simple need to make money– and the communities they interact with can tell.
Yet if you look at the greatest companies out there, you’ll find that they usually have a strong sense of identity and purpose– just like Maslow’s self-actualized people. Read anything by Jim Collins and you’ll see what I mean.
For a recent presentation, Iain developed a chart that looks a lot like the one below. And to embarrass Iain, let’s call it the Gray hierarchy of community needs.
Love, hate, and memo-list
Top management experts are now acknowledging the importance of creating forums and contexts inside corporations that allow peer review, transparency, and powerful natural hierarchies to flourish. Here’s one great post by Gary Hamel from earlier this year that Iain Gray pointed out today. We’ve had an open forum exactly like this at Red Hat for a very long time. We call it memo-list.
When any new employee comes into Red Hat, memo-list is one of the first great shocks to the system. Memo-list itself is not some technological marvel of a collaboration tool– it is just a simple, old skool mailing list where any Red Hat employee can post an email message that goes out to virtually every employee in the company. That’s 3000+ folks.
Memo-list has been a hot issue inside the walls of Red Hat since before I joined ten years ago. Folks tend to either love it or hate it.
Some people are shocked by the fact that any employee can publicly challenge a post by an executive or even the CEO in an email to memo-list (and they do). Some people are annoyed by the discussions that appear over and over, year after year. Some people view it as idle chitchat and a waste of time.
But some people view it as the backbone of the Red Hat culture. A place where the power of meritocracy is nurtured. Where the employees force transparency, openness, and accountability. Where peer review makes for better ideas (after all, given enough eyes, all bugs are shallow).
I love memo-list, warts and all (I think Gary Hamel would like it too). In my view, it is the single most important thing that differentiates the Red Hat culture from most other corporate cultures.
Jim Whitehurst: 5 tips for competing in the 21st century
I spent two days this week at the Coach K Leadership Conference at Duke. It’s always good to get above the trees for a few days, and this experience was exactly that kind of opportunity. Jonathan Opp did a nice summary post on the conference here and you can see the live Twitter stream here.
On Wednesday, Red Hat CEO Jim Whitehurst gave a keynote entitled “Competing as a 21st Century Enterprise Among 20th Century Giants.” Jim comes at this subject from a pretty unique vantage point: he is probably one of the few people in the world who has run both a 20th century company (Delta Airlines, as COO) and a 21st century company (that would be us, Red Hat).
In his presentation, Jim covered some of the things he has learned in moving from the command and control, military-inspired corporate environment of Delta (which is pretty similar to the structure of many of the other great 20th century companies) to the open source-inspired corporate structure here at Red Hat (if you want to learn more about Red Hat and the open source way, here and here and here and here are some posts that will help). In particular, Jim gave five tips that will help your company compete better in the 21st century world– I’ve summarized them below:
Ten people from Red Hat you should follow
Most Twitter users have probably heard of the Twitter tradition of Follow Friday, where you take time on Fridays to introduce your friends to some folks they should be following. Well, I’m lucky to be working alongside some awesome people here at Red Hat, and I thought today I’d introduce you Dark Matter Matters readers to ten Red Hatters who say some pretty smart things online.
 First, meet three members of the Red Hat Community Architecture team. If you are interested in the Red Hat approach to community-building, check out these three rock stars. When it comes to understanding how to build an effective architecture of participation, very few people have more experience or good ideas than Greg, Max, and Karsten.
First, meet three members of the Red Hat Community Architecture team. If you are interested in the Red Hat approach to community-building, check out these three rock stars. When it comes to understanding how to build an effective architecture of participation, very few people have more experience or good ideas than Greg, Max, and Karsten.
1) Greg DeKoenigsberg: Blog | Fedora page | Twitter feed
2) Max Spevack: Blog | Fedora page
3) Karsten Wade: Blog | Fedora page | Twitter feed
As a special bonus, I’m going to introduce you to the newest member of the Community Architecture team, Mel Chua. From what I can tell, Mel may be teaching those three old guys a thing or two about how the next generation will be building community.
Red Hat has a quite a few folks with a deep passion for open source, but when Michael Tiemann, Jan Wildeboer, Venky Hariharan, and Gunnar Hellekson enter the room, their passion takes your breath away (example: I think Jan got a Red Hat tattoo last night– that is passion, man). These guys are great ambassadors for Red Hat, but also for the entire open source movement. Don’t expect any of these four to just toe the corporate line, though– each of them has interests and ideas that extend well beyond the corporate walls.
5) Michael Tiemann: Blog | Web page | Wikipedia entry
6) Jan Wildeboer: Blog | Identi.ca | Twitter
7) Venkatesh Hariharan: Blog
8) Gunnar Hellekson: Blog | Twitter
And finally, closer to home, I want to point you to a couple of folks in the Brand Communications + Design team that I think are doing some really great stuff online. First, my friend and 10-year Red Hat colleague Jonathan Opp, who has begun actively posting on his blog about brand, voice, design, and culture. You will not meet a more talented writer.
9) Jonathan Opp: Blog | Twitter
The last person I want to point out today is BC+D designer Adrienne Yancey. But it’s not her Red Hat work I want to point you to– instead, it’s a really cool blog she writes about food in her spare time. Her photography is beautiful, and it is worth visiting just to drool over the pictures of edamame salad and okra.
10) Adrienne Yancey: Blog
OK, that’s it for today. I’ll try to highlight some other Red Hat folks doing cool stuff online in a later post. After all there are over 3000 of us now working in about 30 countries around the world– there are plenty of great people and ideas to show you.
John Seely Brown’s secret formula for an innovation culture
I spent today at the Coach K Leadership Conference at Duke University (Red Hat CEO Jim Whitehurst will be speaking there tomorrow morning). One of today’s highlights was a panel called “Leading the Creative Enterprise” featuring John Seely Brown (the former director of the famous innovation hub at Xerox PARC).
I always love it when really smart people boil down the world into a simple 2×2 matrix, and during his comments, JSB put a chart up on the screen that looked something like this:
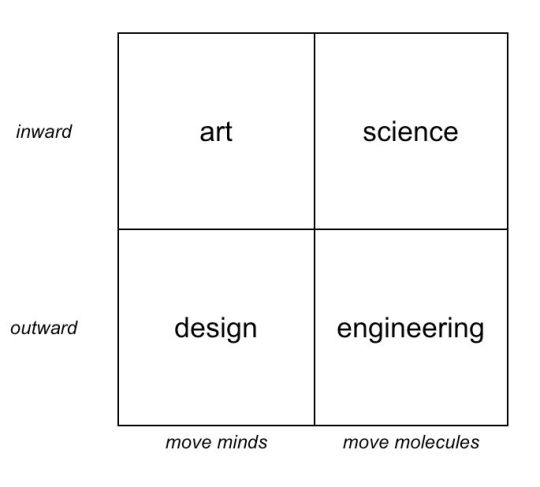 To create a culture that will be successful at innovating, JSB says you must have four types of people: artists, scientists, designers, and engineers working together; each group must be represented.
To create a culture that will be successful at innovating, JSB says you must have four types of people: artists, scientists, designers, and engineers working together; each group must be represented.
Two of the groups (the artists and the scientists) get their energy from the way they internally process their own ideas, while the other two groups (designers and engineers) get their energy by thinking about how those ideas are brought to the outside world.
Looking at the matrix the other way, artists and designers share a common cause of trying to move people’s minds while scientists and engineers are firmly grounded in the world of actually making stuff work beyond the idea itself.
I’ve certainly seen these roles all represented in projects at Red Hat that have resulted in great innovations (the group that worked on the Red Hat values years ago comes to mind). And I’ve also been a part of projects that failed because at least one perspective was missing.
What do you think? Does this matrix work for you?
Banking your community karma for a rainy day
At lunch today, I sat in on a presentation by Red Hat community architect Karsten Wade about open source community-building best practices. Karsten referenced a concept he attributed to Greg DeKoenigsberg, who I believe may be the most talented community architect on the planet. The idea was crazy simple, and it was the first time I’d heard it:
Think of good community work as money you’d put in a bank.
Do really helpful things in the communities you participate in, things that make those communities more successful. If you continue to make these positive karma deposits for a long period of time, the balance in your community karma account will go up. Why do you want a lot of good karma in your account?
For a rainy day, of course!
Every company has times when, for one reason or another, they can’t (or don’t) put their best foot forward. Even the best community citizens (and Red Hat is one of the best, according to Matt Asay “Red Hat is considered the paragon of open-source virtue.”) have bad days.
That is precisely when you make a withdrawal from your community karma account.
If your balance is high, you are more likely to get the benefit of the doubt when trouble arises. If your balance is low or you have a negative balance, well, not so much. If you start making too many withdrawals (i.e. doing a lot of dumb stuff) and don’t make enough deposits, you will start having problems effectively engaging in that community.
I don’t know how that could be any simpler. Or more true. Nice one, Greg.
Tom Sawyer Part 2: where can your company pitch in?
A few weeks ago I wrote a post called Tom Sawyer, whitewashing fences, and building communities online, where I outlined one of the biggest mistakes I see companies make when figuring out their community strategy– they expect a mythical “community” will paint their fence for them. But not everyone is Tom Sawyer.
 If your community strategy starts with the question, “how can I make the community work for me?” you may still find success if there are a bunch of people out there willing to paint your fence for free, but you definitely are not taking advantage of all of the benefits you can get from participating in communities.
If your community strategy starts with the question, “how can I make the community work for me?” you may still find success if there are a bunch of people out there willing to paint your fence for free, but you definitely are not taking advantage of all of the benefits you can get from participating in communities.
One of the most often used examples of customer/community-driven innovation (perhaps because it is simple to understand) is the My Starbucks Idea site. This is a place where customers can tell Starbucks what they want, people vote on each others’ ideas, and Starbucks takes the best ideas and uses them to make their products, services, and experience better.
A recent example of a service that was launched through the site is a mini Starbucks drink card that can fit on your key chain. Sweet. It looks like they’ve had at least 5-10 innovations like this that have come from customer ideas, maybe more. And Starbucks is not alone– many companies have built similar sites, as has The White House. You’ve seen them.
But this approach is still simple Tom Sawyer-style community-building. People just helping Starbucks paint their fence for free. So why is it working for Starbucks? Because there are people out there willing to spend their time and energy helping Starbucks make their products, services, and experience better. Not every brand can command this sort of attention and loyalty. Most can’t, in fact.
My view? I do think these sort of public idea generation efforts are smart 21st century thinking when they work. But why stop there?
I get excited when I see big companies focused not only on what they take from the table, but what they bring to the table. I love to see companies that aren’t afraid to be humble members of communities, rather than building the community around themselves.
Former Red Hat intern is gonna rent out the world
From the we’ll-all-be-working-for-him-someday files:
 Former Red Hat intern and project manager Tim Hyer has been working on a new startup company named Rentcycle. Last night, Techcrunch picked up their story here. Tim worked for us here in the Brand Communications + Design group at Red Hat from 2005 to 2007 and then moved out to the west coast. He is the person most responsible for the hard work of making David Burney‘s design thinking vision come true at Red Hat.
Former Red Hat intern and project manager Tim Hyer has been working on a new startup company named Rentcycle. Last night, Techcrunch picked up their story here. Tim worked for us here in the Brand Communications + Design group at Red Hat from 2005 to 2007 and then moved out to the west coast. He is the person most responsible for the hard work of making David Burney‘s design thinking vision come true at Red Hat.
Rentcycle a pretty neat idea– sign up rental businesses around the country, and then let people rent stuff from one website. See what is in stock at many stores at once, without having to run around a dusty warehouse looking in rusty bins full of candelabras and fine silverware.
Some other folks have tried similar things, but many have tried the Craigslist style approach of one consumer renting to another. Tim’s approach is more B2C (in non-marketing-speak, that means he wants to partner with businesses selling to regular folks), which should make it easier for him to achieve scale without as much pain. My view? Someone’s going to do this right, and knowing Tim, it’s a pretty good bet it will be him.
Follow them on Twitter here or watch their video pitch of the concept (nice stick figure, Tim):
Brand tip: Call a duck a duck
Imagine this: You walk into a pet store, looking for a canary, because, i don’t know, maybe your coal mine is having dirty air issues or something. The salesman, eager to please, walks you over to a cage with a duck sitting in it.
He says, “Do I have just the thing for you, check out this canary. He is a new, better breed of canary. He has webbed feet, can swim, quacks rather than sings, he’s bigger. We call this the web-footed hydro ultracanary. You’ll love him.”
So you buy the “canary” and take him into your coal mine, where he quacks incessantly. In fact, he is still waddling around quacking about ten minutes after you and all of the other miners are lying dead from breathing poisonous air.
In this case, the brand promise (a canary) and the brand experience (a duck with strong lungs) did not match. If you had been looking for a duck, this little guy would have probably been perfect. But as a canary… not so much.
One of my favorite brand rules is to call your ducks ducks. What do I mean? Make things simple for your customers. Don’t make them learn your language or analyze your intent in order to understand your message. Be straight with them.
Brands are like sponges, people
On Twitter yesterday, my friend Chris Blizzard mentioned to someone that I often say “brands are like sponges.” When I saw this, I realized that a) I haven’t said this in a while and b) I should say it more often because it is a freakin’ awesome way to think about brands. So I’m saying it again right now. Right here.
It’s actually not my line. I got it from the Scott Bedbury book A New Brand World (one of the top ten books behind Dark Matter Matters). Near the beginning of the book, Scott, who is one of the masterminds behind the good ol’ days of the Nike brand in the 80s and the Starbucks brand in the 90s, provides one of my favorite definitions of what a brand is:
A brand is the sum of the good, the bad, the ugly, and the off strategy. It is defined by your best product as well as your worst product. It is defined by award-winning advertising as well as by the god-awful ads that somehow slipped through the cracks, got approved, and, not surprisingly, sank into oblivion. It is defined by the accomplishments of your best employee– the shining star in the company who can do no wrong– as well as by the mishaps of the worst hire that you ever made. It is also defined by your receptionist and the music your customers are subjected to when they are placed on hold. For every grand and finely worded public statement by the CEO, the brand is also defined by derisory consumer comments overheard in the hallway or in a chat room on the Internet. Brands are sponges for content, for images, for fleeting feelings. They become psychological concepts held in the minds of the public, where they may stay forever. As such, you can’t entirely control a brand. At best you can only guide and influence it.
Those last two lines have stuck in my mind since I first read them. First, the idea that a brand is a sponge, soaking up everything, both good and bad. And second, that you cannot control a brand, you can only guide and influence it.







